Finokalia Atmospheric Observatory FKL
for Research and Education on the Environment since 1993
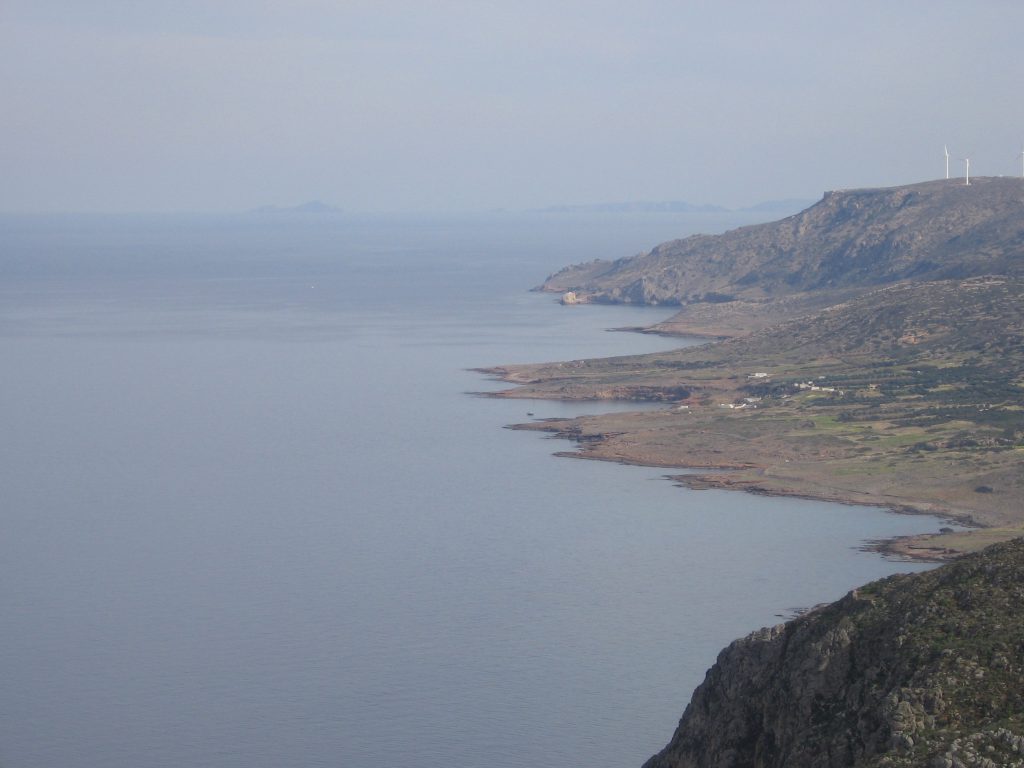
35o 20' N, 25o 40' E, 250 m asl
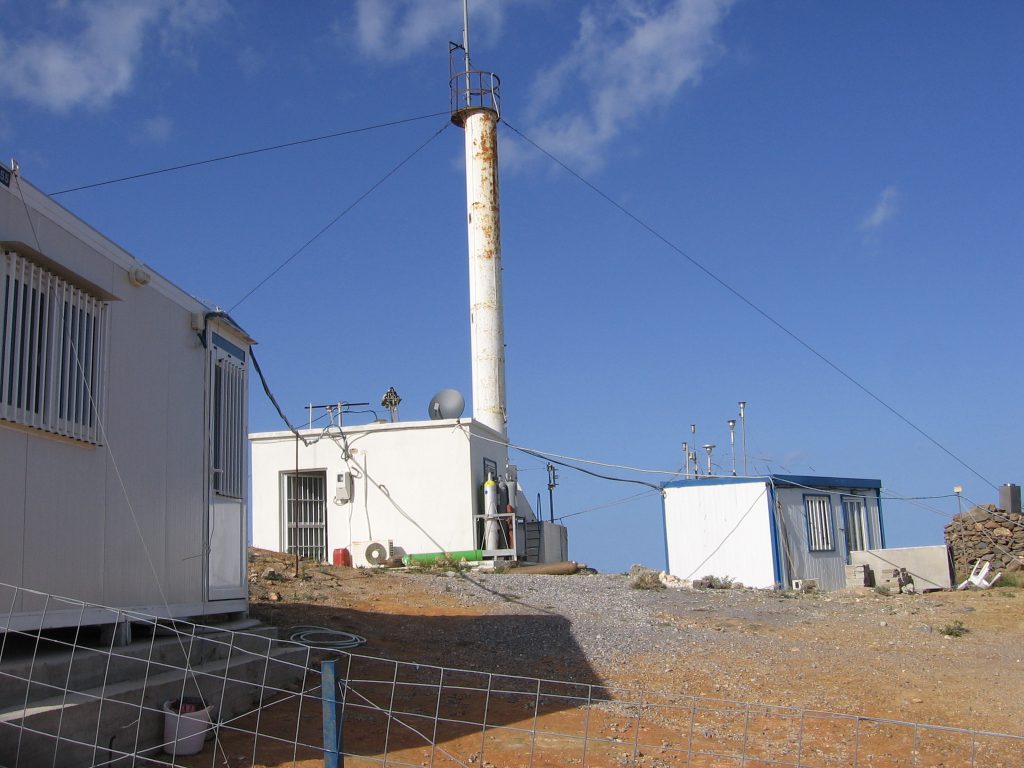
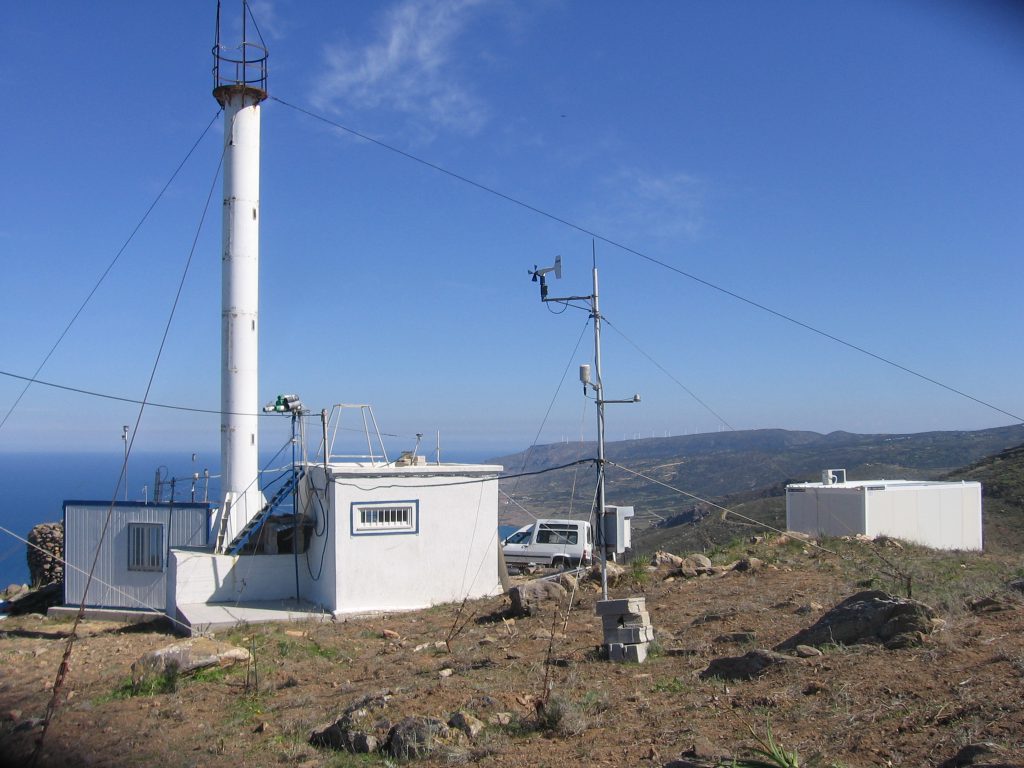
The Finokalia atmospheric monitoring station is operated by the Environmental Chemical Processes Laboratory (ECPL) of the Department of Chemistry of the University of Crete since 1993. The station is representative for the Eastern Mediterranean atmosphere and has attracted strong scientific attention in the fields of atmospheric composition, air quality and climate change. It also reports to authorities as the regional background station for Greece. The station has currently the longest time series of CO2 and CH4 greenhouse gases observations in the East Mediterranean and together with Agia Marina in Cyprus the longest ozone record in the region. The station is hosting innovative field experiments and provides TransNational Access to researchers from abroad to perform targeted experiments complementary to the observations performed at Finokalia from ECPL. The uniqueness of the station is reflected in the numerous scientific publications, post graduate and doctoral theses, scientific projects conducted at the site, and its participation in the most important international research infrastructures and networks of environmental research stations, like ACTRIS, ICOS, GAW, EMEP.
Trans-National Access
Highlights
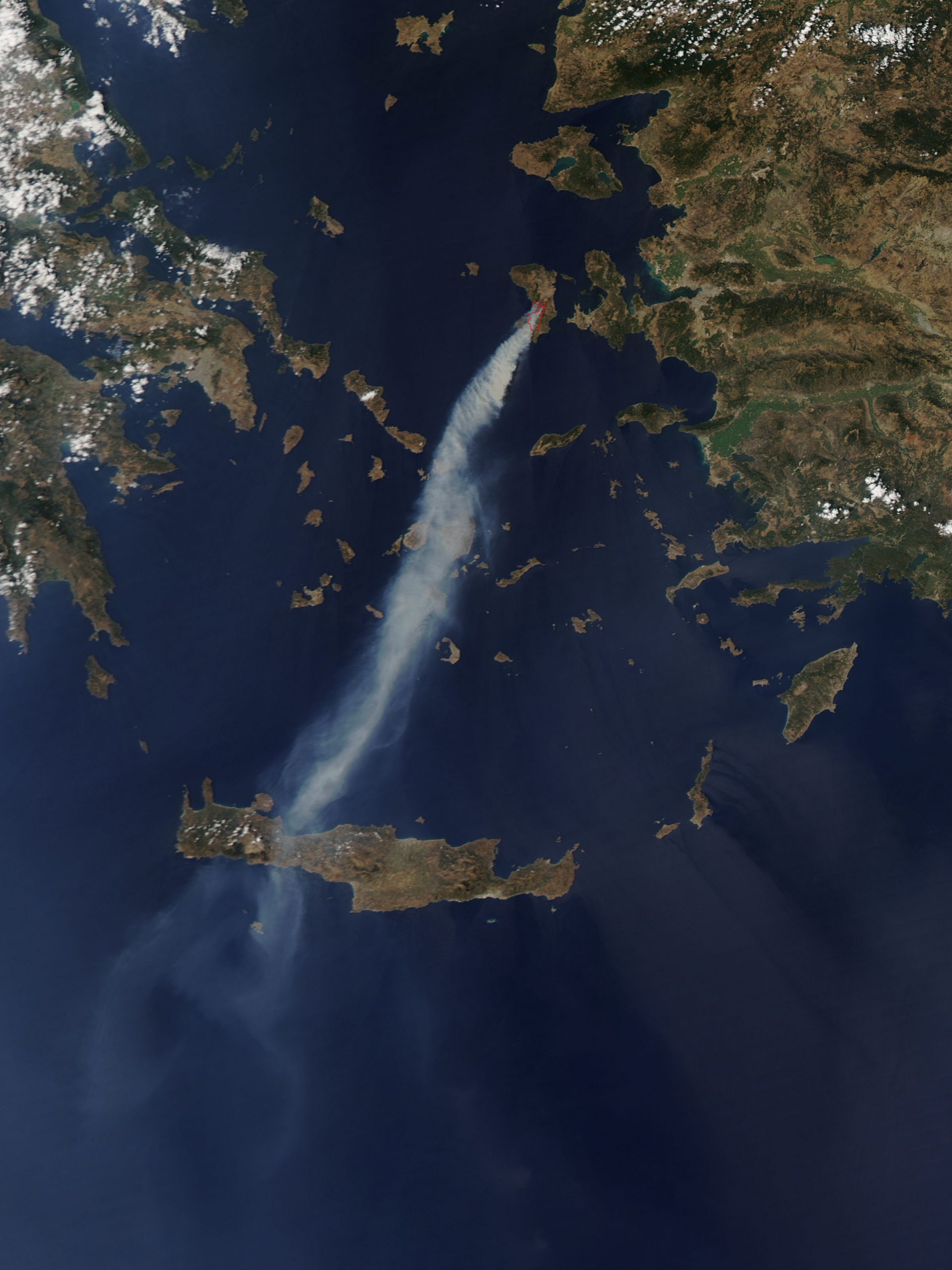
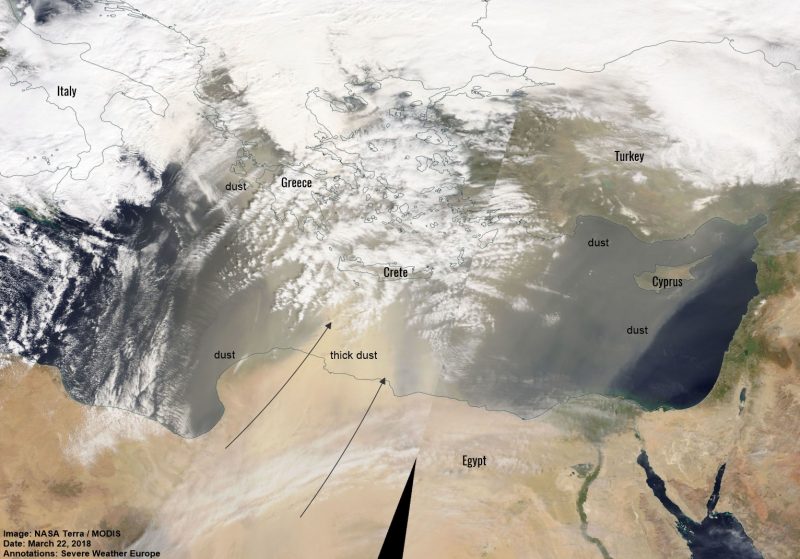
Finokalia observatory located in the East Mediterranean at the cross-road of air masses from the European, Asian and African continents is sporadically affected by African intense dust outbreaks with extraordinary high levels of particulate matter (PM) also seen by satellites (left panel) that affect visibility, population at risk, the radiation balance of the atmosphere and, through atmospheric deposition, the ecosystems’ functioning. The strongest African dust outbreak event recorded during the last decade at Finokalia was observed on March 22, 2018, when PM10 levels as high as 6300 μg/m3 (5 minutes values) have been measured.
The station is also well located to observe air pollution from any large open fires mainly from continental Greece and Turkey that are occurring in the surrounding region during summer. The impact of the fires is seen in the measured Black Carbon levels. The impact of both large dust outbreaks and open fires in the area is also seen by satellites.